Prostate Cancer
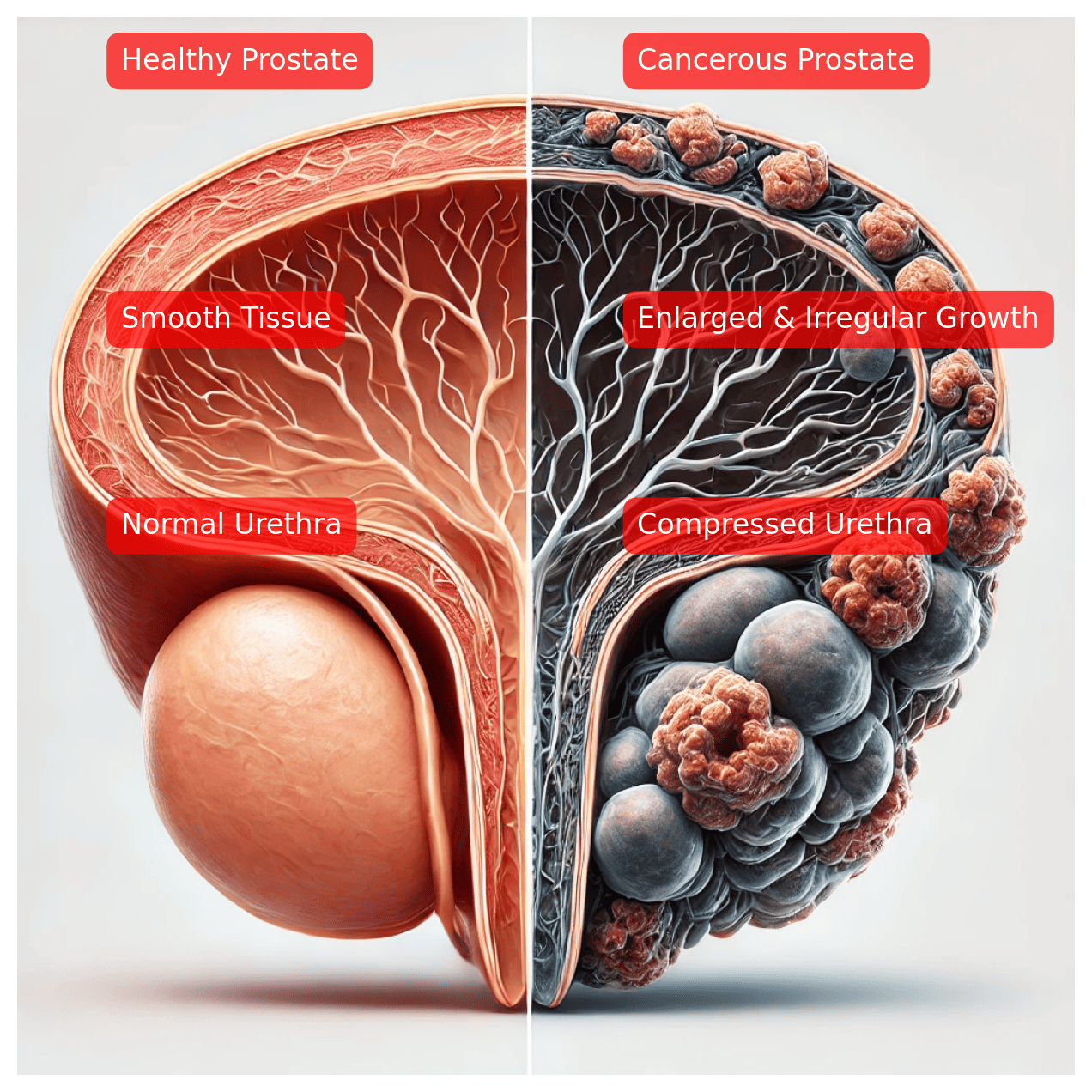
Prostate cancer is a type of cancer that develops in the prostate gland. The prostate is a small chestnut-sized gland found in men. It produces fluids that nourish and transport sperm. It makes sperm healthy or fertile for conception.
Prostate cancer is the growth of tumours developed inside the prostate gland in men. It grows slowly and stays in the prostate without causing harm, or it spreads quickly with a harmful effect. When discovered early, while it remains in the prostate gland, it provides the opportunity for a successful treatment before it spreads.
Source:
https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/prostate-enlargement/
What are the Symptoms of Prostate Cancer?
Prostate cancer may cause no signs or symptoms in its early stages. However, when not detected early and as it progresses, you may begin to see signs and symptoms such as:
- Trouble urinating
- Erectile dysfunction
- Painful ejaculation
- Reduced force in the stream of urine
- Blood in the semen
- Feeling pain in the chest, hips, or lower back
- Swelling of the prostate gland
- Feeling pain in the testicles
- Weight loss
- Blood in the urine
- Pain when you pee
Other medical conditions have similar symptoms as prostate cancer. Therefore, do not get worried or feel sad when you discover a growth in your organ or experience any of these signs. Consult first with your doctor to examine and detect your condition. The condition can be:
- Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH): This is a condition that makes your prostate larger without increasing the risk of cancer. Everyone with a prostate is likely to develop Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH).
- Prostatitis: is a condition that causes the swelling and inflammation of your prostate gland. It is usually caused by bacterial infections. It often occurs in men younger than 50 years of age.
How Do I Know I Have Prostate cancer?
There are some personalized symptoms of prostate cancer such as regular urination, finding it difficult to start or stop urine flow, presence of blood in urine or semen. You might also feel pain in the lower back, hips, and pelvic area.
However, they do not always mean you have prostate cancer. If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, ensure you see a healthcare professional for proper evaluation.
Tests to Diagnose Prostate Cancer
Testing or screening for prostate cancer aims to identify it before it spreads. One of the ways to identify prostate cancer is to do a biopsy. A Biopsy is a surgery that involves taking tiny pieces of the prostate to look with a microscope. If the test results show the presence of cancer cells, the next step is to discuss treatment options with your doctor.
Another screening test you can use to identify prostate cancer is a prostate-specific antigen (PSA) blood test.
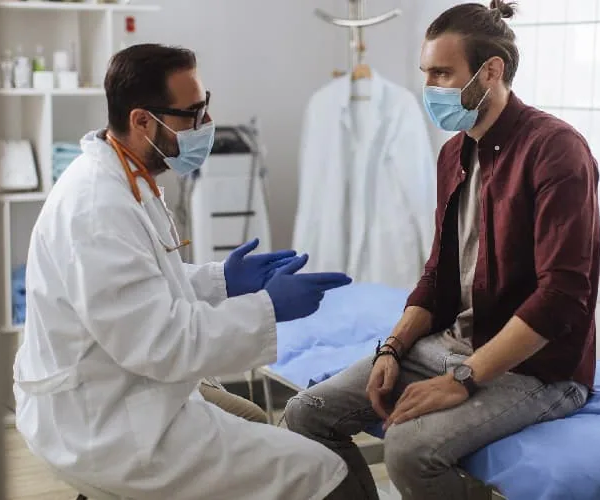

Source: https://www.cdc.gov/prostate-cancer/screening/.
This test measures the amount of prostate-specific antigen (PSA) available in your blood. The prostate produces prostate-specific antigen by the prostate. If you have a high level of PSA in your blood, you have a great tendency to have prostate cancer.
Digital Rectal Exam (DRE): It is a test carried out by a healthcare professional to check for any abnormalities in the prostate gland. The test can be used to identify any sign of prostate infection. If your healthcare provider thinks you may have an infection, more testing will be done to help guide your treatment.
Imaging Tests: It can be ultrasound, MRI, or CT scans. They may be used for further evaluation of the prostate and surrounding tissues for any signs of cancer spread.
What are the risk factors of Prostate Cancer?
Factors that can contribute to the risk of having prostate cancer are:
- Gender
- Age: Prostate cancer is common in older age. A man who is above 50 years of age is at risk of prostate cancer.
- Family history: if you have a blood relative who has been diagnosed with prostate cancer, it might increase the risk of you having it. It could be your parent, child, or sibling. A strong family host of breast cancer can also increase the risk of prostate cancer.

- Race: Black people have a higher risk of prostate cancer than other races.
- Weight (obesity): Being overweight contributes to raising the risk of prostate cancer. It is necessary to maintain a healthy weight to live a healthy life.
What are the Complications of Prostate Cancer?
The complications of prostate cancer are:
- Urinary continence: prostate cancer and the treatment options can cause urinary continence. It refers to the inability to control your bladder.
- Erectile dysfunction
- Spread of cancer: prostate cancer can spread to the bones or nearby organs such as the bladder. If transported through the bloodstream to your bones, it can cause broken bones or pain. When prostate cancer spreads to another organ, it may be controlled or respond to treatment but is not likely to be
Treatment of prostate cancer includes:
- Close monitoring and follow-up visits: this type of treatment is used for older men who do not have symptoms of prostate cancer. The doctor and the nurse keep an eye on the patient to see any symptoms of the condition. During the observation, the patient undergoes tests such as a PSA test, and biopsy to find out if the cancer is growing. Treatment is given when the cancer cells begin to grow to relieve the symptoms and improve the patient’s health.
- Radiation – the use of high-energy X-rays and other types of radiation to stop the growth of cancer cells or kill the cancer cells.
- Surgery to remove the prostate: There are however side effects from getting surgery or radiation. They include:
-
- Infertility or impotence.
- Loss of bladder control.
- Problems with your rectum.
- Loss of desire for sex
- Sexual organ might become less effective
- Hormone therapy: this involves the removal of male hormones to stop cancer cells from growing. Medications or surgeries are used to achieve this.
- Chemotherapy: It also involves the use of medications to hinder the growth of cancer cells in the prostate.
- Supplements: Taking supplements may reduce the risk of developing prostate cancer or for its treatment. They include selenium, calcium, lycopene, green tea, vitamins D & E, and others. These supplements are used to promote men’s prostate health.
How Do I Prevent Prostate Cancer?
- Exercise: try to exercise regularly. Studies showed how regular exercise can lower the development and complications of prostate cancer. Exercising also helps to maintain your weight and improves your mood and general well-being. If you are new to exercising, start with a slow routine and be consistent with it till you increase it.
- Eat healthy foods: Choose to eat healthy foods and diet with vegetables and fruits. By eating a healthy diet, you can improve your general health. Vegetables and fruits contain vitamins and nutrients that can improve your health.
- Maintain a healthy weight: Work out and eat a healthy diet to maintain your weight if it is presently healthy. If you need to lose weight, exercise regularly and follow the guidance of a gym instructor and doctor.
- Medications: Medications are considered for men with high risks of prostate cancer. Discuss with your healthcare professional if you have an increased risk of prostate cancer or you are living with prostate cancer.

 Browse Categories
Browse Categories 

